ABA Accessibility Standard for GSA Facilities Pocket Guide
ABA CHAPTER 1: APPLICATION AND ADMINISTRATION
F101 Purpose
This document contains scoping and technical requirements for accessibility to sites, facilities, buildings, and elements by individuals with disabilities. The requirements are to be applied during the design, construction, addition to, alteration, and lease of sites, facilities, buildings, and elements to the extent required by regulations issued by Federal agencies under the Architectural Barriers Act of 1968 (ABA).
Federal agencies must design distinctive and high quality Federal facilities that meet all of the following standards:
(b) Provide individuals with disabilities ready access to, and use of, the facilities in accordance with the standards in Sec. 102-76.65 (the ABAAS; see Introduction to this pocket guide).
(a) The Architectural Barriers Act applies to any facility that is intended for use by the public or that may result in the employment or residence therein of individuals with disabilities, which is to be--
(1) Constructed or altered by, or on behalf of, the United States;
(2) Leased in whole or in part by the United States;
(3) Financed in whole or in part by a grant or loan made by the United States, if the building or facility is subject to standards for design, construction, or alteration issued under the authority of the law authorizing such a grant or loan; or
(4) Constructed under the authority of the National Capital Transportation Act of 1960, the National Capital Transportation Act of 1965, or Title III of the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Regulation Compact.
(b) The Architectural Barriers Act does not apply to any privately owned residential facility unless leased by the Government for subsidized housing programs, and any facility on a military reservation designed and constructed primarily for use by able bodied military personnel.
F102 Dimensions for Adults and Children
The technical requirements are based on adult dimensions and anthropometrics. In addition, this document includes technical requirements based on children's dimensions and anthropometrics for drinking fountains, water closets, toilet compartments, lavatories and sinks, dining surfaces, and work surfaces.
F103 Modifications and Waivers
The Architectural Barriers Act authorizes the Administrator of the General Services Administration, the Secretary of the Department of Housing and Urban Development, the Secretary of the Department of Defense, and the United States Postal Service to modify or waive the accessibility standards for buildings and facilities covered by the Architectural Barriers Act on a case-by-case basis, upon application made by the head of the department, agency, or instrumentality of the United States concerned. The General Services Administration, the Department of Housing and Urban Development, the Department of Defense, and the United States Postal Service may grant a modification or waiver only upon a determination that it is clearly necessary. Section 502(b)(1) of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 authorizes the Access Board to ensure that modifications and waivers are based on findings of fact and are not inconsistent with the Architectural Barriers Act.
Advisory F103 Modifications and Waivers. The provisions for modifications and waivers differ from the requirement issued under the Americans with Disabilities Act in that "equivalent facilitation" does not apply. There is a formal procedure for Federal agencies to request a waiver or modification of applicable standards under the Architectural Barriers Act.
(a) The head of each Federal agency must ensure that documentation is maintained on each contract, grant or loan for the design, construction or alteration of a facility and on each lease for a facility subject to the standards in Sec. 102-76.65(a) containing one of the following statements:
(1) The standards have been or will be incorporated in the design, the construction or the alteration.
(2) The grant or loan has been or will be made subject to a requirement that the standards will be incorporated in the design, the construction or the alteration.
(3) The leased facility meets the standards, or has been or will be altered to meet the standards.
(4) The standards have been waived or modified by the Administrator of General Services, and a copy of the waiver or modification is included with the statement.
(b) If a determination is made that a facility is not subject to the standards in Sec. 102-76.65(a) because the Architectural Barriers Act does not apply to the facility, the head of the Federal agency must ensure that documentation is maintained to justify the determination.
F104 Conventions
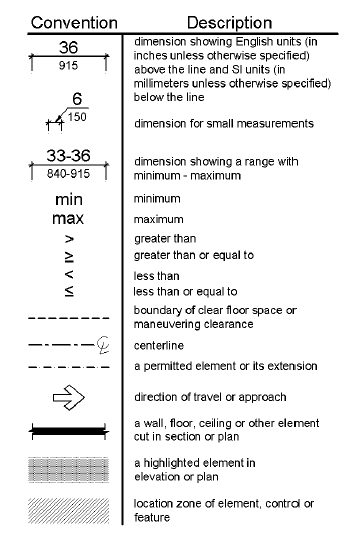
Figure F104
Graphic Convention for Figures
F104.1 Dimensions.
Dimensions that are not stated as "maximum" or "minimum" are absolute.
F104.1.1 Construction and Manufacturing Tolerances.
All dimensions are subject to conventional industry tolerances except where the requirement is stated as a range with specific minimum and maximum end points.
Advisory F104.1.1 Construction and Manufacturing Tolerances. Conventional industry tolerances recognized by this provision include those for field conditions and those that may be a necessary consequence of a particular manufacturing process. Recognized tolerances are not intended to apply to design work.
It is good practice when specifying dimensions to avoid specifying a tolerance where dimensions are absolute. For example, if this document requires "1½ inches," avoid specifying "1½ inches plus or minus X inches."
Where the requirement states a specified range, such as in 609.4 where grab bars must be installed between 33 inches and 36 inches above the floor, the range provides an adequate tolerance and therefore no tolerance outside of the range at either end point is permitted.
Where a requirement is a minimum or a maximum dimension that does not have two specific minimum and maximum end points, tolerances may apply. Where an element is to be installed at the minimum or maximum permitted dimension, such as "15 inches minimum" or "5 pounds maximum," it would not be good practice to specify "5 pounds (plus X pounds) or 15 inches (minus X inches)." Rather, it would be good practice to specify a dimension less than the required maximum (or more than the required minimum) by the amount of the expected field or manufacturing tolerance and not to state any tolerance in conjunction with the specified dimension.
Specifying dimensions in design in the manner described above will better ensure that facilities and elements accomplish the level of accessibility intended by these requirements. It will also more often produce an end result of strict and literal compliance with the stated requirements and eliminate enforcement difficulties and issues that might otherwise arise. Information on specific tolerances may be available from industry or trade organizations, code groups and building officials, and published references.
F104.2 Calculation of Percentages.
Where the required number of elements or facilities to be provided is determined by calculations of ratios or percentages and remainders or fractions result, the next greater whole number of such elements or facilities shall be provided. Where the determination of the required size or dimension of an element or facility involves ratios or percentages, rounding down for values less than one half shall be permitted.
F104.3 Figures.
Unless specifically stated otherwise, figures are provided for informational purposes only.
F105.1 General.
The standards listed in F105.2 are incorporated by reference in this document and are part of the requirements to the prescribed extent of each such reference. The Director of the Federal Register has approved these standards for incorporation by reference in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR part 51. Copies of the referenced standards may be inspected at the Architectural and Transportation Barriers Compliance Board, 1331 F Street, NW, Suite 1000, Washington, DC 20004; at the Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division, Disability Rights Section, 1425 New York Avenue, NW, Washington, DC; at the Department of Transportation, 400 Seventh Street, SW, Room 10424, Washington DC; or at the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). For information on the availability of this material at NARA, call (202) 741-6030, or go to http://www.archives.gov/federal_register/code_of_federal_regulations/ibr_locations.html.
F105.2 Referenced Standards.
The specific editions of the standards listed below are referenced in this document. Where differences occur between this document and the referenced standards, this document applies.
F105.2.1 ANSI/BHMA.
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association, 355 Lexington Avenue, 17th floor, New York, NY 10017 (http://www.buildershardware.com).
ANSI/BHMA A156.10-1999 American National Standard for Power Operated Pedestrian Doors (see 404.3).
ANSI/BHMA A156.19-1997 American National Standard for Power Assist and Low Energy Power Operated Doors (see 404.3, 408.3.2.1, and 409.3.1).
ANSI/BHMA A156.19-2002 American National Standard for Power Assist and Low Energy Power Operated Doors (see 404.3, 408.3.2.1, and 409.3.1).
Advisory F105.2.1 ANSI/BHMA. ANSI/BHMA A156.10-1999 applies to power operated doors for pedestrian use which open automatically when approached by pedestrians. Included are provisions intended to reduce the chance of user injury or entrapment.
ANSI/BHMA A156.19-1997 and A156.19-2002 applies to power assist doors, low energy power operated doors or low energy power open doors for pedestrian use not provided for in ANSI/BHMA A156.10 for Power Operated Pedestrian Doors. Included are provisions intended to reduce the chance of user injury or entrapment.
F105.2.2 ASME.
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York, New York 10016 (http://www.asme.org).
ASME A17.1- 2000 Safety Code for Elevators and Escalators, including ASME A17.1a-2002 Addenda and ASME A17.1b-2003 Addenda (see 407.1, 408.1, 409.1, and 810.9).
ASME A18.1-1999 Safety Standard for Platform Lifts and Stairway Chairlifts, including ASME A18.1a-2001 Addenda and ASME A18.1b-2001 Addenda (see 410.1).
ASME A18.1-2003 Safety Standard for Platform Lifts and Stairway Chairlifts (see 410.1).
Advisory F105.2.2 ASME. ASME A17.1-2000 is used by local jurisdictions throughout the United States for the design, construction, installation, operation, inspection, testing, maintenance, alteration, and repair of elevators and escalators. The majority of the requirements apply to the operational machinery not seen or used by elevator passengers. ASME A17.1 requires a two-way means of emergency communications in passenger elevators. This means of communication must connect with emergency or authorized personnel and not an automated answering system. The communication system must be push button activated. The activation button must be permanently identified with the word "HELP." A visual indication acknowledging the establishment of a communications link to authorized personnel must be provided. The visual indication must remain on until the call is terminated by authorized personnel. The building location, the elevator car number, and the need for assistance must be provided to authorized personnel answering the emergency call. The use of a handset by the communications system is prohibited. Only the authorized personnel answering the call can terminate the call. Operating instructions for the communications system must be provided in the elevator car.
The provisions for escalators require that at least two flat steps be provided at the entrance and exit of every escalator and that steps on escalators be demarcated by yellow lines 2 inches wide maximum along the back and sides of steps.
ASME A18.1-1999 and ASME A18.1-2003 address the design, construction, installation, operation, inspection, testing, maintenance and repair of lifts that are intended for transportation of persons with disabilities. Lifts are classified as: vertical platform lifts, inclined platform lifts, inclined stairway chairlifts, private residence vertical platform lifts, private residence inclined platform lifts, and private residence inclined stairway chairlifts.
This document does not permit the use of inclined stairway chairlifts which do not provide platforms because such lifts require the user to transfer to a seat.
ASME A18.1 contains requirements for runways, which are the spaces in which platforms or seats move. The standard includes additional provisions for runway enclosures, electrical equipment and wiring, structural support, headroom clearance (which is 80 inches minimum), lower level access ramps and pits. The enclosure walls not used for entry or exit are required to have a grab bar the full length of the wall on platform lifts. Access ramps are required to meet requirements similar to those for ramps in Chapter 4 of this document.
Each of the lift types addressed in ASME A18.1 must meet requirements for capacity, load, speed, travel, operating devices, and control equipment. The maximum permitted height for operable parts is consistent with 308 of this document. The standard also addresses attendant operation. However, 410.1 of this document does not permit attendant operation.
F105.2.3 ASTM.
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the American Society for Testing and Materials, 100 Bar Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania 19428 (http://www.astm.org).
ASTM F 1292-99 Standard Specification for Impact Attenuation of Surface Systems Under and Around Playground Equipment (see 1008.2.6.2).
ASTM F 1292-04 Standard Specification for Impact Attenuation of Surfacing Materials Within the Use Zone of Playground Equipment (see 1008.2.6.2).
ASTM F 1487-01 Standard Consumer Safety Performance Specification for Playground Equipment for Public Use (see F106.5).
ASTM F 1951-99 Standard Specification for Determination of Accessibility of Surface Systems Under and Around Playground Equipment (see 1008.2.6.1).
Advisory F105.2.3 ASTM. ASTM F 1292-99 and ASTM F 1292-04 establish a uniform means to measure and compare characteristics of surfacing materials to determine whether materials provide a safe surface under and around playground equipment. These standards are referenced in the play areas requirements of this document when an accessible surface is required inside a play area use zone where a fall attenuating surface is also required. The standards cover the minimum impact attenuation requirements, when tested in accordance with Test Method F 355, for surface systems to be used under and around any piece of playground equipment from which a person may fall.
ASTM F 1487-01 establishes a nationally recognized safety standard for public playground equipment to address injuries identified by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. It defines the use zone, which is the ground area beneath and immediately adjacent to a play structure or play equipment designed for unrestricted circulation around the equipment and on whose surface it is predicted that a user would land when falling from or exiting a play structure or equipment. The play areas requirements in this document reference the ASTM F 1487 standard when defining accessible routes that overlap use zones requiring fall attenuating surfaces. If the use zone of a playground is not entirely surfaced with an accessible material, at least one accessible route within the use zone must be provided from the perimeter to all accessible play structures or components within the playground.
ASTM F 1951-99 establishes a uniform means to measure the characteristics of surface systems in order to provide performance specifications to select materials for use as an accessible surface under and around playground equipment. Surface materials that comply with this standard and are located in the use zone must also comply with ASTM F 1292. The test methods in this standard address access for children and adults who may traverse the surfacing to aid children who are playing. When a surface is tested it must have an average work per foot value for straight propulsion and for turning less than the average work per foot values for straight propulsion and for turning, respectively, on a hard, smooth surface with a grade of 7% (1:14).
F105.2.4 ICC/IBC.
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the International Code Council, 5203 Leesburg Pike, Suite 600, Falls Church, Virginia 22041 (http://www.iccsafe.org).
International Building Code, 2000 Edition (see F207.1, F207.2, F216.4.2, F216.4.3, and 1005.2.1).
International Building Code, 2001 Supplement (see F207.1 and F207.2).
International Building Code, 2003 Edition (see F207.1, F207.2, F216.4.2, F216.4.3, and 1005.2.1).
Advisory F105.2.4 ICC/IBC. International Building Code (IBC)-2000 (including 2001 Supplement to the International Codes) and IBC-2003 are referenced for means of egress, areas of refuge, and railings provided on fishing piers and platforms. At least one accessible means of egress is required for every accessible space and at least two accessible means of egress are required where more than one means of egress is required. The technical criteria for accessible means of egress allow the use of exit stairways and evacuation elevators when provided in conjunction with horizontal exits or areas of refuge. While typical elevators are not designed to be used during an emergency evacuation, evacuation elevators are designed with standby power and other features according to the elevator safety standard and can be used for the evacuation of individuals with disabilities. The IBC also provides requirements for areas of refuge, which are fire-rated spaces on levels above or below the exit discharge levels where people unable to use stairs can go to register a call for assistance and wait for evacuation.
The recreation facilities requirements of this document reference two sections in the IBC for fishing piers and platforms. An exception addresses the height of the railings, guards, or handrails where a fishing pier or platform is required to include a guard, railing, or handrail higher than 34 inches (865 mm) above the ground or deck surface.
F105.2.5 NFPA.
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the National Fire Protection Association, 1 Batterymarch Park, Quincy, Massachusetts 02169-7471, (http://www.nfpa.org).
NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm Code, 1999 Edition (see 702.1 and 809.5.2).
NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm Code, 2002 Edition (see 702.1 and 809.5.2).
Advisory F105.2.5 NFPA. NFPA 72-1999 and NFPA 72-2002 address the application, installation, performance, and maintenance of protective signaling systems and their components. The NFPA 72 incorporates Underwriters Laboratory (UL) 1971 by reference. The standard specifies the characteristics of audible alarms, such as placement and sound levels. However, 702 of these requirements limits the volume of an audible alarm to 110 dBA, rather than the maximum 120 dBA permitted by NFPA 72-1999.
NFPA 72 specifies characteristics for visible alarms, such as flash frequency, color, intensity, placement, and synchronization. However, Section 702 of this document requires that visual alarm appliances be permanently installed. UL 1971 specifies intensity dispersion requirements for visible alarms. In particular, NFPA 72 requires visible alarms to have a light source that is clear or white and has polar dispersion complying with UL 1971.
F106.1 General.
For the purpose of this document, the terms defined in F106.5 have the indicated meaning.
Advisory F106.1 General. Terms defined in F106.5 are italicized in the text of this document.
ETA Editor’s Note
Selected defined terms from the GSA Final Rule are double underlined in the text of this document.
F106.2 Terms Defined in Referenced Standards.
Terms not defined in F106.5 or in regulations issued by the Administrator of the General Services Administration, the Secretary of Defense, the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development, or the United States Postal Service to implement the Architectural Barriers Act but specifically defined in a referenced standard, shall have the specified meaning from the referenced standard unless otherwise stated.
F106.3 Undefined Terms.
The meaning of terms not specifically defined in F106.5 or in regulations issued by the Administrator of the General Services Administration, the Secretary of Defense, the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development, or the United States Postal Service to implement the Architectural Barriers Act or in referenced standards shall be as defined by collegiate dictionaries in the sense that the context implies.
F106.4 Interchangeability.
Words, terms and phrases used in the singular include the plural and those used in the plural include the singular.
F106.5 Defined Terms.
Accessible.
A site, building, facility, or portion thereof that complies with this part.
Accessible Means of Egress.
A continuous and unobstructed way of egress travel from any point in a building or facility that provides an accessible route to an area of refuge, a horizontal exit, or a public way.
Addition.
An expansion, extension, or increase in the gross floor area or height of a building or facility.
Administrative Authority.
A governmental agency that adopts or enforces regulations and guidelines for the design, construction, or alteration of buildings and facilities.
Alteration.
A change to a building or facility that affects or could affect the usability of the building or facility or portion thereof. Alterations include, but are not limited to, remodeling, renovation, rehabilitation, reconstruction, historic restoration, resurfacing of circulation paths or vehicular ways, changes or rearrangement of the structural parts or elements, and changes or rearrangement in the plan configuration of walls and full-height partitions. Normal maintenance, reroofing, painting or wallpapering, or changes to mechanical and electrical systems are not alterations unless they affect the usability of the building or facility. [ECTCR UFAS 3.5]
Alteration. Remodeling, improving, extending, or making other changes to a facility, exclusive of maintenance repairs that are preventive in nature. The term includes planning, engineering, architectural work and other similar actions. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Amusement Attraction.
Any facility, or portion of a facility, located within an amusement park or theme park which provides amusement without the use of an amusement device. Amusement attractions include, but are not limited to, fun houses, barrels, and other attractions without seats.
Amusement Ride.
A system that moves persons through a fixed course within a defined area for the purpose of amusement.
Amusement Ride Seat.
A seat that is built-in or mechanically fastened to an amusement ride intended to be occupied by one or more passengers.
Area of Sport Activity.
That portion of a room or space where the play or practice of a sport occurs.
Assembly Area.
A building or facility, or portion thereof, used for the purpose of entertainment, educational or civic gatherings, or similar purposes. For the purposes of these requirements, assembly areas include, but are not limited to, classrooms, lecture halls, courtrooms, public meeting rooms, public hearing rooms, legislative chambers, motion picture houses, auditoria, theaters, playhouses, dinner theaters, concert halls, centers for the performing arts, amphitheaters, arenas, stadiums, grandstands, or convention centers.
Assistive Listening System (ALS).
An amplification system utilizing transmitters, receivers, and coupling devices to bypass the acoustical space between a sound source and a listener by means of induction loop, radio frequency, infrared, or direct-wired equipment.
Boarding Pier.
A portion of a pier where a boat is temporarily secured for the purpose of embarking or disembarking.
Boards.
Boards include, but are not limited to, wood, plastic, metal, and composite products.
Boat Launch Ramp.
A sloped surface designed for launching and retrieving trailered boats and other water craft to and from a body of water.
Boat Slip.
That portion of a pier, main pier, finger pier, or float where a boat is moored for the purpose of berthing, embarking, or disembarking.
Building.
Any structure used or intended for supporting or sheltering any use or occupancy.
Camp Shelter.
A partially enclosed structure that provides campers and hikers cover from weather and that does not contain plumbing fixtures or kitchen appliances. Camp shelters are not transient lodging facilities or residential dwelling units.
Camping Facility.
A site, or portion of a site, developed for outdoor recreational purposes that contains camping units.
Camping Unit.
An outdoor space in a camping facility used for camping that contains outdoor constructed features, parking spaces for recreational vehicles or other vehicles, tent pads or tent platforms, or camp shelters.
Catch Pool.
A pool or designated section of a pool used as a terminus for water slide flumes.
Characters.
Letters, numbers, punctuation marks and typographic symbols.
Children's Use.
Describes spaces and elements specifically designed for use primarily by people 12 years old and younger.
Circulation Path.
An exterior or interior way of passage provided for pedestrian travel, including but not limited to, walks, hallways, courtyards, elevators, platform lifts, ramps, stairways, and landings.
Closed-Circuit Telephone.
A telephone with a dedicated line such as a house phone, courtesy phone or phone that must be used to gain entry to a facility.
Common Use.
Interior or exterior circulation paths, rooms, spaces, or elements that are not for public use and are made available for the shared use of two or more people. [ECTCR UFAS 3.5]
Cross Slope.
The slope that is perpendicular to the direction of travel (see running slope).
Curb Ramp.
A short ramp cutting through a curb or built up to it.
Detectable Warning.
A standardized surface feature built in or applied to walking surfaces or other elements to warn of hazards on a circulation path.
Element.
An architectural or mechanical component of a building, facility, space, or site.
Elevated Play Component.
A play component that is approached above or below grade and that is part of a composite play structure consisting of two or more play components attached or functionally linked to create an integrated unit providing more than one play activity.
Employee Work Area.
All or any portion of a space used only by employees and used only for work. Corridors, toilet rooms, kitchenettes and break rooms are not employee work areas.
Entrance.
Any access point to a building or portion of a building or facility used for the purpose of entering. An entrance includes the approach walk, the vertical access leading to the entrance platform, the entrance platform itself, vestibule if provided, the entry door or gate, and the hardware of the entry door or gate.
Facility.
All or any portion of buildings, structures, site improvements, elements, and pedestrian routes or vehicular ways located on a site.
Federal Agency. Any Executive agency or any establishment in the legislative or judicial branch of the Government (except the Senate, the House of Representatives, and the Architect of the Capitol and any activities under his or her direction). (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Foot-candle. The illumination on a surface one square foot in area on which there is a uniformly distributed flux of one lumen, or the illuminance produced on a surface all points of which are at a distance of one foot from a directionally uniform point source of one candela. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Gangway.
A variable-sloped pedestrian walkway that links a fixed structure or land with a floating structure. Gangways that connect to vessels are not addressed by this document.
Golf Car Passage.
A continuous passage on which a motorized golf car can operate.
Ground Level Play Component.
A play component that is approached and exited at the ground level.
GSA. The U.S. General Services Administration, acting by or through the Administrator of General Services, or a designated official to whom functions under this part have been delegated by the Administrator of General Services. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Joint Use.
Interior or exterior rooms, spaces, or elements that are common space available for use by all occupants of the building. Joint use does not include mechanical or custodial rooms or areas occupied by other tenants.
Lease.
Any agreement which establishes the relationship of landlord and tenant.
Mail Boxes.
Receptacles for the receipt of documents, packages, or other deliverable matter. Mail boxes include, but are not limited to, post office boxes and receptacles provided by commercial mail-receiving agencies, apartment facilities, or schools.
Marked Crossing.
A crosswalk or other identified path intended for pedestrian use in crossing a vehicular way.
Mezzanine.
An intermediate level or levels between the floor and ceiling of any story with an aggregate floor area of not more than one-third of the area of the room or space in which the level or levels are located. Mezzanines have sufficient elevation that space for human occupancy can be provided on the floor below.
Military Installation.
A base, camp, post, station, yard, center, homeport facility for any ship, or other activity or operation under the jurisdiction of the Department of Defense, including any leased facility. Military installation does not include any facility used primarily for civil works, rivers and harbors projects, or flood control projects. Multiple, contiguous, or collocated bases, camps, posts, stations, yards, centers, or home ports shall not be considered as constituting a single military installation.
Occupant Load.
The number of persons for which the means of egress of a building or portion of a building is designed.
Operable Part.
A component of an element used to insert or withdraw objects, or to activate, deactivate, or adjust the element.
Outdoor Constructed Features.
Picnic tables, fire rings, grills, fireplaces, wood stoves, trash and recycling receptacles, water hydrants, utility and sewage hookups, outdoor rinsing showers, benches, and viewing scopes provided at outdoor recreation facilities.
Picnic Facility.
A site, or portion of a site, developed for outdoor recreational purposes that contains picnic units.
Picnic Unit.
An outdoor space in a picnic facility used for picnicking that contains outdoor constructed features.
Pictogram.
A pictorial symbol that represents activities, facilities, or concepts.
Play Area.
A portion of a site containing play components designed and constructed for children.
Play Component.
An element intended to generate specific opportunities for play, socialization, or learning. Play components are manufactured or natural; and are stand-alone or part of a composite play structure.
Public Building. (1) Any building that is suitable for office and/or storage space for the use of one or more Federal agencies or mixed-ownership corporations, such as Federal office buildings, post offices, customhouses, courthouses, border inspection facilities, warehouses, and any such building designated by the President. It also includes buildings of this sort that are acquired by the Federal Government under the Administrator's installment-purchase, lease-purchase, and purchase-contract authorities.
(2) Public building does not include buildings:
(i) On the public domain.
(ii) In foreign countries.
(iii) On Indian and native Eskimo properties held in trust by the United States.
(iv) On lands used in connection with Federal programs for agricultural, recreational, and conservation purposes.
(v) On or used in connection with river, harbor, flood control, reclamation or power projects, or for chemical manufacturing or development projects, or for nuclear production, research, or development projects.
(vi) On or used in connection with housing and residential projects.
(vii) On military installations.
(viii) On Department of Veterans Affairs installations used for hospital or domiciliary purposes.
(ix) Excluded by the President. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Public Entrance.
An entrance that is not a service entrance or a restricted entrance.
Public Use.
Interior or exterior rooms, spaces, or elements that are made available to the public. Public use may be provided at a building or facility that is privately or publicly owned.
Public Way.
Any street, alley or other parcel of land open to the outside air leading to a public street, which has been deeded, dedicated or otherwise permanently appropriated to the public for public use and which has a clear width and height of not less than 10 feet (3050 mm).
Qualified Historic Building or Facility.
A building or facility that is listed in or eligible for listing in the National Register of Historic Places or designated as historic under an appropriate State or local law.
Ramp.
A walking surface that has a running slope steeper than 1:20.
Repairs. Those additions or changes that are necessary for the protection and maintenance of property to deter or prevent excessive or rapid deterioration or obsolescence, and to restore property damaged by storm, flood, fire, accident, or earthquake. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Residential Dwelling Unit.
A unit intended to be used as a residence that is primarily long-term in nature. Residential dwelling units do not include transient lodging, inpatient medical care, licensed long-term care, and detention or correctional facilities.
Restricted Entrance.
An entrance that is made available for common use on a controlled basis but not public use and that is not a service entrance.
Running Slope.
The slope that is parallel to the direction of travel (see cross slope).
Self-Service Storage.
Building or facility designed and used for the purpose of renting or leasing individual storage spaces to customers for the purpose of storing and removing personal property on a self-service basis.
Service Entrance.
An entrance intended primarily for delivery of goods or services.
Site.
A parcel of land bounded by a property line or a designated portion of a public right-of-way.
Soft Contained Play Structure.
A play structure made up of one or more play components where the user enters a fully enclosed play environment that utilizes pliable materials, such as plastic, netting, or fabric.
Space.
A definable area, such as a room, toilet room, hall, assembly area, entrance, storage room, alcove, courtyard, or lobby.
State. The fifty States, political subdivisions thereof, the District of Columbia, the Commonwealths of Puerto Rico and Guam, and the territories and possessions of the United States. (41 CFR, Chapter 102, Subchapter C, Part 102-71, Sec. 102-71.20 What definitions apply to GSA's real property policies?)
Story.
That portion of a building or facility designed for human occupancy included between the upper surface of a floor and upper surface of the floor or roof next above. A story containing one or more mezzanines has more than one floor level.
Structural Frame.
The columns and the girders, beams, and trusses having direct connections to the columns and all other members that are essential to the stability of the building or facility as a whole.
Tactile.
An object that can be perceived using the sense of touch.
Technically Infeasible.
With respect to an alteration of a building or a facility, something that has little likelihood of being accomplished because existing structural conditions would require removing or altering a load-bearing member that is an essential part of the structural frame; or because other existing physical or site constraints prohibit modification or addition of elements, spaces, or features that are in full and strict compliance with the minimum requirements.
Teeing Ground.
In golf, the starting place for the hole to be played.
Trail.
A pedestrian route developed primarily for outdoor recreational purposes. A pedestrian route developed primarily to connect elements, spaces, or facilities within a site is not a trail.
Trailhead.
An outdoor space that is designated by an entity responsible for administering or maintaining a trail to serve as an access point to the trail. The junction of two or more trails or the undeveloped junction of a trail and a road is not a trailhead.
Transfer Device.
Equipment designed to facilitate the transfer of a person from a wheelchair or other mobility aid to and from an amusement ride seat.
Transient Lodging.
A building or facility containing one or more guest room(s) for sleeping that provides accommodations that are primarily short-term in nature. Transient lodging does not include residential dwelling units intended to be used as a residence, inpatient medical care facilities, licensed long-term care facilities, detention or correctional facilities, or private buildings or facilities that contain not more than five rooms for rent or hire and that are actually occupied by the proprietor as the residence of such proprietor.
Transition Plate.
A sloping pedestrian walking surface located at the end(s) of a gangway.
TTY.
An abbreviation for teletypewriter. Machinery that employs interactive text-based communication through the transmission of coded signals across the telephone network. TTYs may include, for example, devices known as TDDs (telecommunication display devices or telecommunication devices for deaf persons) or computers with special modems. TTYs are also called text telephones
Use Zone.
The ground level area beneath and immediately adjacent to a play structure or play equipment that is designated by ASTM F 1487 (incorporated by reference, see "Referenced Standards" in Chapter 1) for unrestricted circulation around the play equipment and where it is predicted that a user would land when falling from or exiting the play equipment.
Vehicular Way.
A route provided for vehicular traffic, such as in a street, driveway, or parking facility.
Viewing Area.
An outdoor space developed for viewing landscapes, wildlife, or other points of interest.
Walk.
An exterior prepared surface for pedestrian use, including pedestrian areas such as plazas and courts.
Wheelchair Space.
Space for a single wheelchair and its occupant.
Work Area Equipment.
Any machine, instrument, engine, motor, pump, conveyor, or other apparatus used to perform work. As used in this document, this term shall apply only to equipment that is permanently installed or built-in in employee work areas subject to the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA). Work area equipment does not include passenger elevators and other accessible means of vertical transportation.

User Comments/Questions
Add Comment/Question