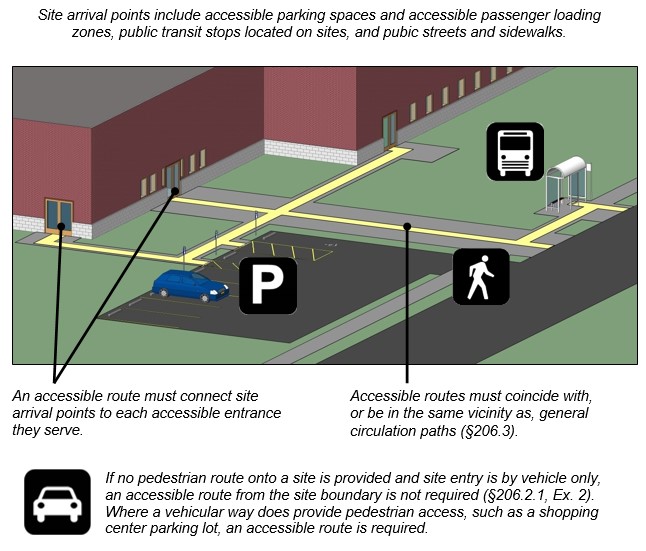
Where Required: Site Arrival Points [§206.2.1]
This guide explains scoping and technical requirements for accessible routes in the ADA Standards.
At least one accessible route must be provided within the site to accessible facility entrances from these site arrival points, where provided:
-
accessible parking and accessible passenger loading zones
-
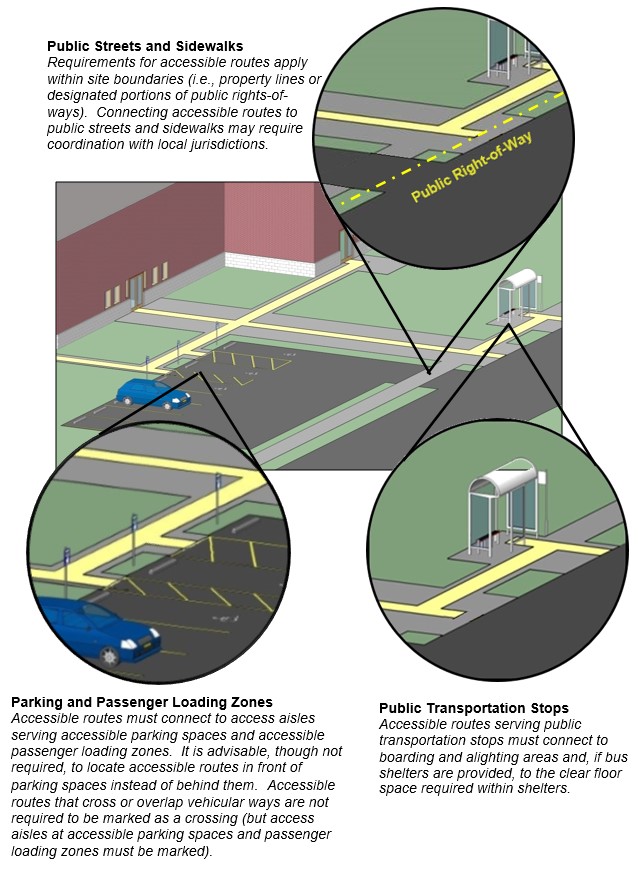
public streets and sidewalks
-
each public transportation stop.
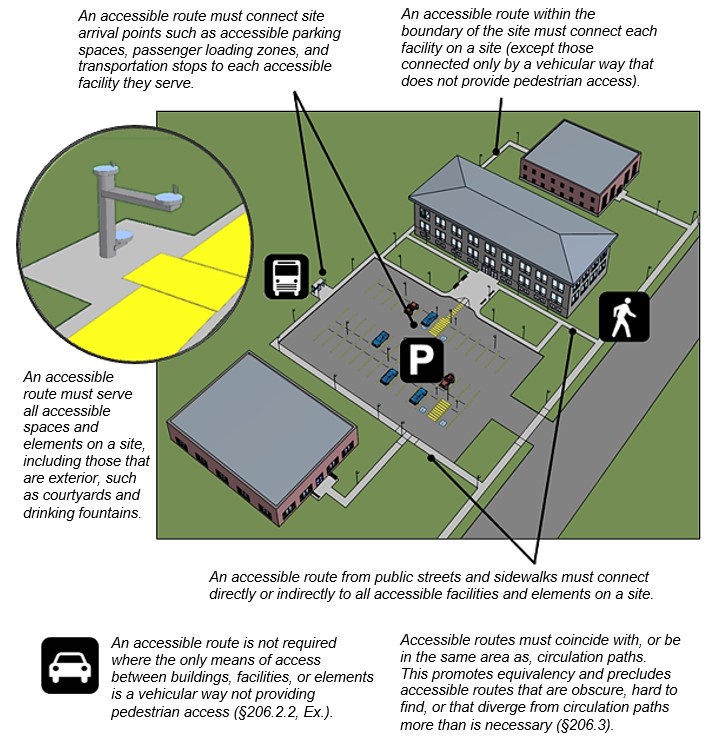
Accessible Routes within a Site [§206.2.2]
At least one accessible route within the boundary of the site originating from site arrival points must connect all accessible buildings, facilities, elements, and spaces on a site.
Accessible Routes (Exterior) within a Site
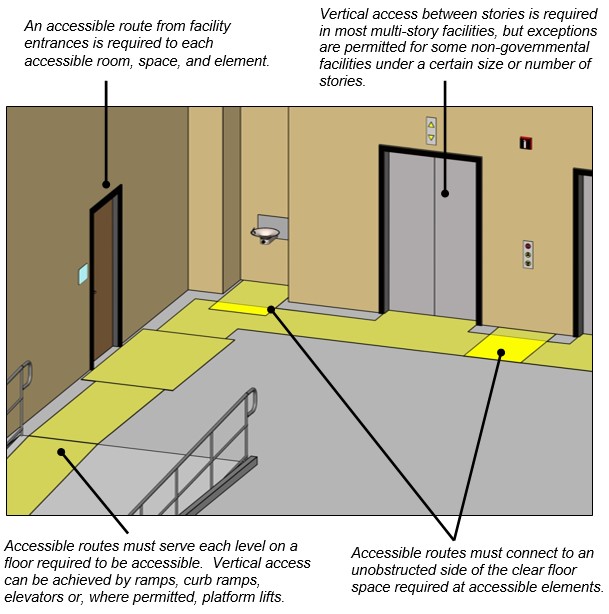
Accessible Routes within a Building or Facility
At least one accessible route must connect all accessible spaces and elements. If a circulation path is interior, the accessible route also must be interior. Accessible vertical interior circulation must be in the same area as stairs and escalators, not isolated in the back of the facility.
In alterations and additions, an accessible route is required where circulation paths are altered or built (§202.3). Also, alterations or additions to areas containing a primary function (a major activity for which a facility is intended) require an accessible path of travel that extends to site arrival points to the extent that the additional cost does not exceed 20% (§202.4). Otherwise, if a space or element is altered, but the circulation path to it is not, an accessible route is not required.


User Comments/Questions
Add Comment/Question