Introduction
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 recognizes and protects the civil rights of people with disabilities and is modeled after earlier landmark laws prohibiting discrimination on the basis of race and gender. The ADA covers a wide range of disability, from physical conditions affecting mobility, stamina, sight, hearing, and speech to conditions such as emotional illness and learning disorders. The ADA addresses access to the workplace (title I), state and local government services (title II), and places of public accommodation and commercial facilities (title III). It also requires phone companies to provide telecommunications relay services for people who have hearing or speech impairments (title IV) and miscellaneous instructions to Federal agencies that enforce the law (title V).
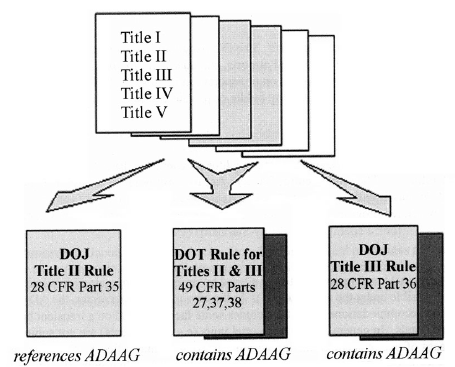
Regulations that set requirements and establish enforcement procedures are necessary to implement laws such as the ADA. To understand and comply with the ADA, it is important to follow the regulations issued under the different titles. Comprehensive regulations for titles II and III issued by the Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Department of Transportation (DOT) include enforceable standards for the construction and alteration of buildings and facilities. These standards, which are based on the ADA Accessibility Guidelines (ADAAG), are enforced by DOJ, DOT and the courts and apply nationwide. The regulations provide important information on which buildings and facilities are subject to the standards. It is important that the regulations be used along with the design standards they contain or reference.
Private Sector Title III covers two types of facilities: places of public accommodation and commercial facilities. The DOJ regulation for title III defines these facilities and those that are exempt (religious entities and private clubs). This regulation contains enforceable standards based on ADAAG and addresses certain provisions in the standards (e.g., elevator exception, alterations to primacy function areas).
State and Local Governments State and local government facilities are addressed in regulations issued by DOJ under title II. This regulation references standards based on ADAAG and allows the option of an earlier standard, the Uniform Federal Accessibility Standards (UFAS).
Public Transportation Facilities The DOT regulation covers public transit facilities such as bus stops and stations, rail stations, and airports. Standards in this regulation are based on ADAAG and include a special occupancy section on transportation facilities. The DOT regulations also include standards for transit vehicles operated by public or private entities.
Federal Facilities The ADA does not address Federal facilities because they are covered by earlier federal laws. The Architectural Barriers Act of 1968 requires access to buildings designed, built, altered, or leased with federal funds. The Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (section 504) requires access to federally funded programs and services. ADAAG derives in part from the standards used under these laws, the Uniform Federal Accessibility Standards (UFAS).
Housing All housing constructed or altered by or on behalf of state or local governments is required to be accessible under the ADA (title II). In the case of the private sector, the ADA's coverage of places of public accommodations (title III) includes some facilities used on a transient basis, such as dormitories and hotels. In general, other residential units (e.g., apartments) are not subject to the ADA except for places of public accommodation within them (e.g., rental offices). Note that distinctions made for purposes of ADA coverage do not coincide with typical building code classifications of "residential" occupancies. Access to housing is also required by the Fair Housing Amendments Act of 1988. This applies to privately and publicly owned buildings and includes guidelines for multi-family housing. The Department of Housing and Urban Development can provide further information on this law and its design requirements (see page 4).






User Comments/Questions
Add Comment/Question